Broadly there are 4 levels of measurement for the variables 1. An example of the ratio level of measurement is weight.
What Is The Difference Between Ordinal Interval And Ratio
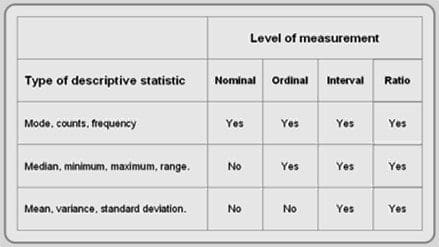
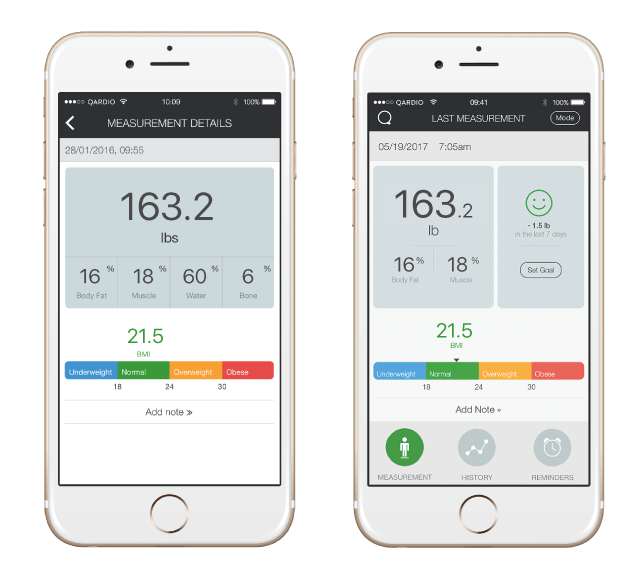
What level of measurement is body weight. Data at the ratio level possess all of the features of the interval level in addition to a zero value. At lower levels of measurement assumptions tend to be less restrictive and data analyses tend to be less sensitive. Can be used in computations. We can calculate ratios like these because the scale for weight in pounds starts at zero pounds. Your body fat percentage is the percentage of your weight that comes from fat. Can be measured in kilograms pounds etc.
We can compare these values on a number line. Can be measured in centimeters inches feet etc. Skin fold calipers are a common method of measuring body fat percentage but you may not have access to calipers. These variables have a natural order. Phrases such as four times and twice are meaningful at the ratio level. The fourth and highest level of measurement is the ratio level.
You can also measure body fat percentage with a scale and tape measure. And cannot have a value below zero. 2 pounds is less than 4 pounds you can take a mathematical average of these values ie. At each level up the hierarchy the current level includes all of the qualities of the one below it and adds something new. A high bmi can be an indicator of high body fatness. Variables that can be measured on a ratio scale have the following properties.
Something we can measure with a tool or a scale or count. Bmi can be used to screen for weight categories that may lead to health problems but it is not diagnostic of the body fatness or health of an individual. Its important to recognize that there is a hierarchy implied in the level of measurement idea. Most modern body composition laboratories today use the value of 11 kilograms per litre for the density of the fat free mass a theoretical tissue composed of 72 water density 0993 21 protein density 1340 and 7 mineral density 3000 by weight. Quantitative numerical values representing counts or measures. Due to the presence of a zero it now makes sense to compare the ratios of measurements.
2097 01069 x height in centimeters 02466 x weight in kilograms total body weight tbw in liters to get the percentage of water in your body assume 1 liter equals 1 kilogram and then. Body mass index bmi is a persons weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters. And cannot have a value below zero. A person who weights 150 pounds weights twice as much as a person who weighs only 75 pounds and half as much as a person who weighs 300 pounds. The level of measurement of a variable is nothing but the mathematical nature of a variable or how a variable is measured. 3 types of data.
The nominal level variables are organized into non numeric categories that cannot be ranked or compared quantitatively.






/losing-inches-but-not-losing-weight-1231559_color1-5b75e98146e0fb0025807d84.png)


/GettyImages-639710428-590507315f9b5810dcca6dcb.jpg)