Measurement of plasma volume requires a tracer which is mostly limited to this compartment and this is achieved by using a tracer which binds to albumin. Chisholm gd waterworth pm calnan js garrod lp.
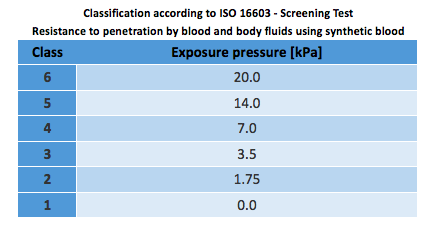
How Well Do You Understand En 14126 2003 Protection Against
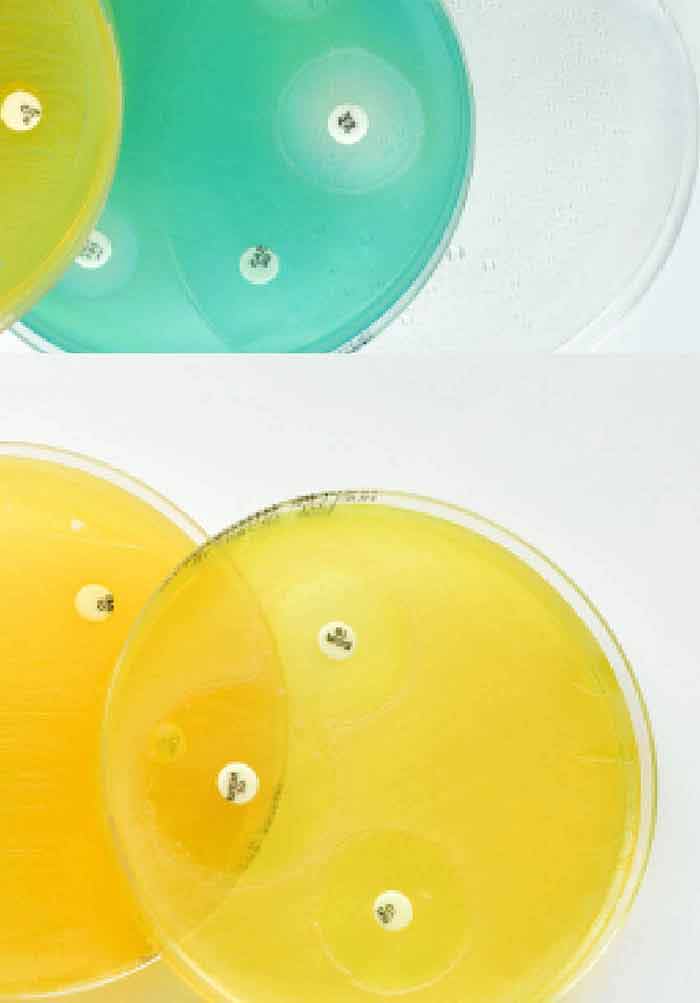
Measurement of antimicrobial agents levels in body fluids. Concentration of antibacterial agents in interstitial tissue fluid. A simple micro agar diffusion method for the determination of antibiotic concentrations in blood and other body fluids. The bioactive antibiotic levels in the pleural fluid and in the serum were measured by a commercial laboratory microbiology reference laboratories. Applications significance of and methods for the measurement of antimicrobial concentrations in human body fluids the measurement of antibiotic concentrations in various fluids has been a prominent aspect of the evaluation of new antibiotics and the quality control of their manufacture. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids. 1921504 indexed for medline publication types.
Cypress ca using a microbiological assay. 12 with this assay the antibiotic levels are determined by comparing the amount of bacterial inhibition present in the sample to the amount of bacterial inhibition present in standard specimens with known antibiotic concentrations. Use of antibiotics to measure amount of antimicrobial agents. Constitutive inducible produced at low level wo stimulus. With the development of various assay techniques the total amount of antimicrobial agent in serum as well as in urine cerebrospinal fluid csf and other body fluids can be measured. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids biological assys immunoassays.
Production greatly increased after. Measurement of antimicrobial agents in serum and body fluids biologic assays. The tracers used are the azo dye known as evans blue or t1824 which binds avidly to albumin or radio iodine labelled serum albumin risa. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobial agents is important to ensure that therapeutic levels have been obtained and to avoid excessive levels of potentially toxic agents such as aminoglycosides and glycopeptides especially when renal function is compromised. Pmc free article georgopoulos a. Focus on finding the biologically active amount of drug immunoassays.
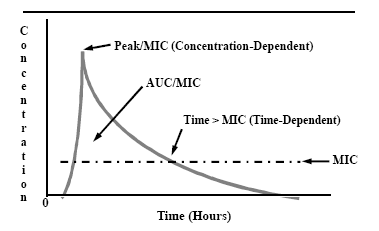
In contrast dilution methods allow determination of the minimal inhibitory concentration of an agent which can be correlated with blood urine and other body fluid levels of the antimicrobial agent. The measurement of the antibiotic concentration in body fluids and tissue samples makes it possible to determine whether the drug concentration at the site of infection is high enough when compared with the mic value and thus to predict the therapeutic effect. Accurate measurement of serum concentrations of antimicrobial agents is important when the margin between therapeutic and toxic levels is narrow such as for aminoglycosides or vancomycin and when a patient has renal failure and may have accumulation of high levels of antimicrobial agents.