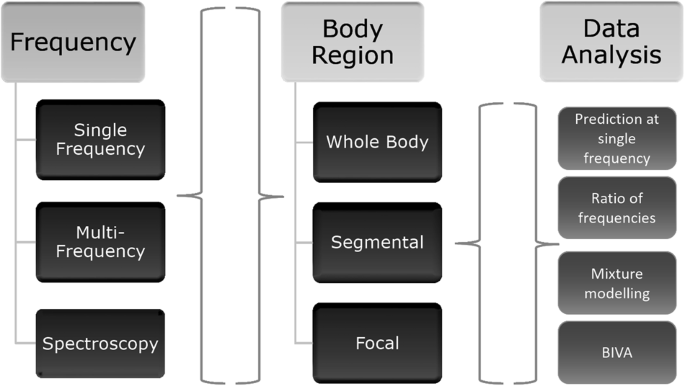
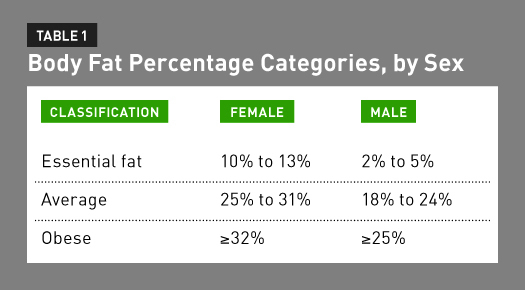
Bioelectrical impedance analysis bia definition. Because water is a good conductor of electricity the current travels easily through parts of your body composed mostly of water muscle and less easily through fat.
/GettyImages-E003605-5675c8233df78ccc151e4a4b.jpg)
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Definition And Tips
Body fat measurement bioelectrical impedance. Since the advent of the first commercially available devices. Body fat adipose tissue causes greater resistance impedance than fat free mass and slows the rate at which the current travels. As the electrical conductivity is different between various bodily tissues eg. Bioelectrical impedance analysis bia is a method for measuring body composition based on the rate at which an electrical current travels through the body. However the convienience of this method comes at a price of accuracy. Bioelectrical impedance analysis bia is a relatively simple quick and non invasive technique to measure body composition.
Bioelectrical impedance analysis bia determines body composition by running small electrical currents through the body. Muscle fat bone etc due to their variation in water content the small electrical current passes through the tissues at different speeds. Most body water is stored in muscle. According to the acsm bioelectric impedance analysis bia works by passing a low intensity electric current through the body and measuring its resistance. This method is commonly used in bathroom scales and handheld devices that measure percent body fat. Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a commonly used method for estimating body composition in particular body fat and muscle mass.
In bia a weak electric current flows through the body and the voltage is measured in order to calculate impedance of the body. Bioelectrical impedance bia bia is one of the quickest and easiest methods for predicting body fat. Therefore if a person is more muscular there is a high chance that the person will also have more body water which leads to lower impedance. Bia involves running a light electrical current through your body. It measures body fat accurately in controlled clinical conditions but its performance in the field is inconsistent. The faster the current travels from one lead to another the more muscle and less fat the person has.